Note
This tutorial is generated from a Jupyter notebook that can be downloaded and run interactively.
Surface reconstruction#
In many scenarios we want to generate a dense 3D geometry, i.e., a triangle mesh. However, from a multi-view stereo method, or a depth sensor we only obtain an unstructured point cloud. To get a triangle mesh from this unstructured input we need to perform surface reconstruction. In the literature there exists a couple of methods and CloudViewer currently implements the following:
Alpha shapes [Edelsbrunner1983]
Ball pivoting [Bernardini1999]
Poisson surface reconstruction [Kazhdan2006]
Alpha shapes#
The alpha shape [Edelsbrunner1983] is a generalization of a convex hull. As described here one can intuitively think of an alpha shape as the following: Imagine a huge mass of ice cream containing the points \(S\) as hard chocolate pieces. Using one of these sphere-formed ice cream spoons we carve out all parts of the ice cream block we can reach without bumping into chocolate pieces, thereby even carving out holes in the inside (e.g., parts not reachable by simply moving the spoon from the outside). We will eventually end up with a (not necessarily convex) object bounded by caps, arcs and points. If we now straighten all round faces to triangles and line segments, we have an intuitive description of what is called the alpha shape of \(S\).
CloudViewer implements the method create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape that involves the tradeoff parameter alpha.
[2]:
bunny = cv3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh = cv3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
pcd = mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(750)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
alpha = 0.03
print(f"alpha={alpha:.3f}")
mesh = cv3d.geometry.ccMesh.create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape(pcd, alpha)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_back_face=True)
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW Error: X11: The DISPLAY environment variable is missing
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
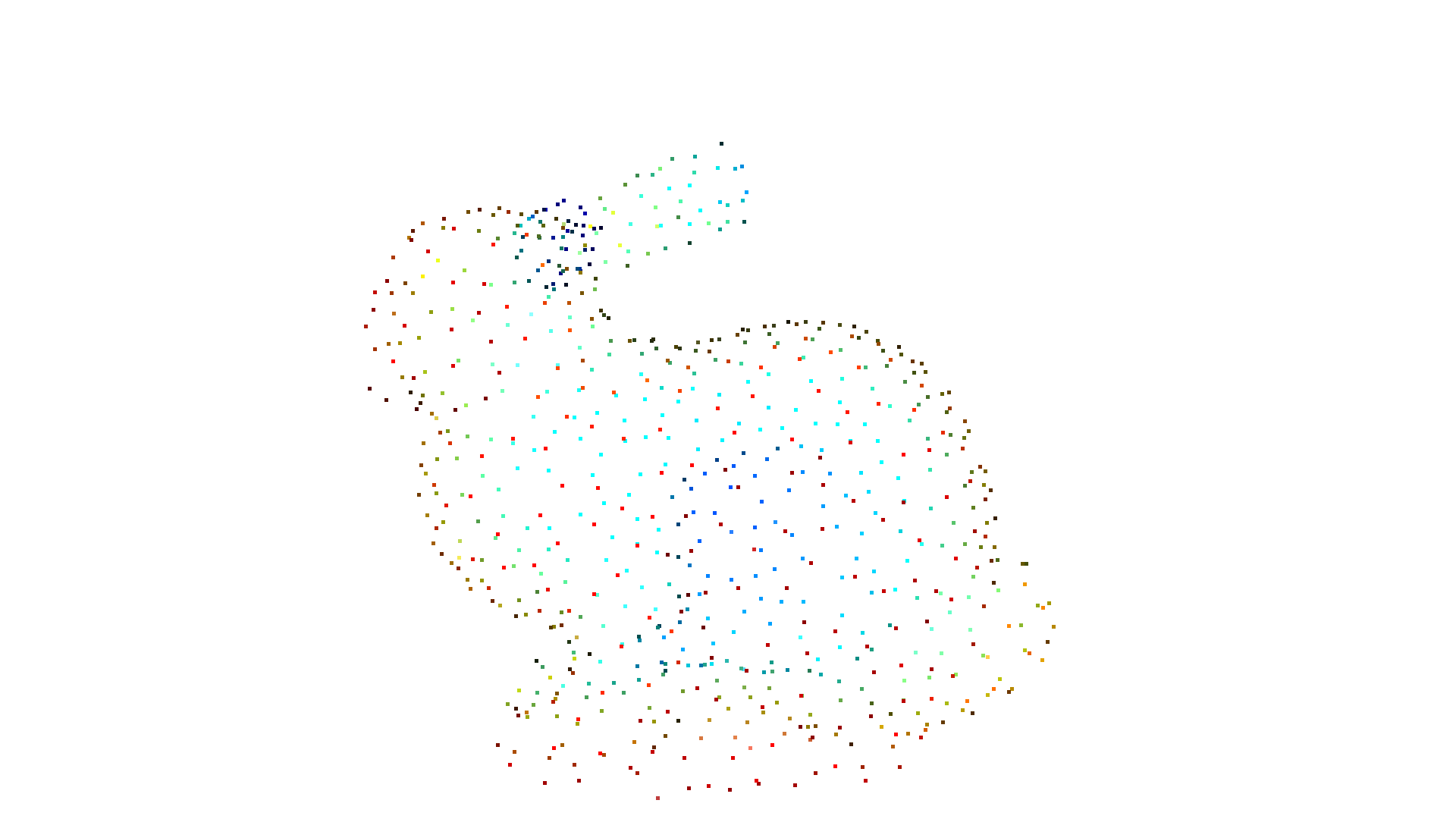
alpha=0.030
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
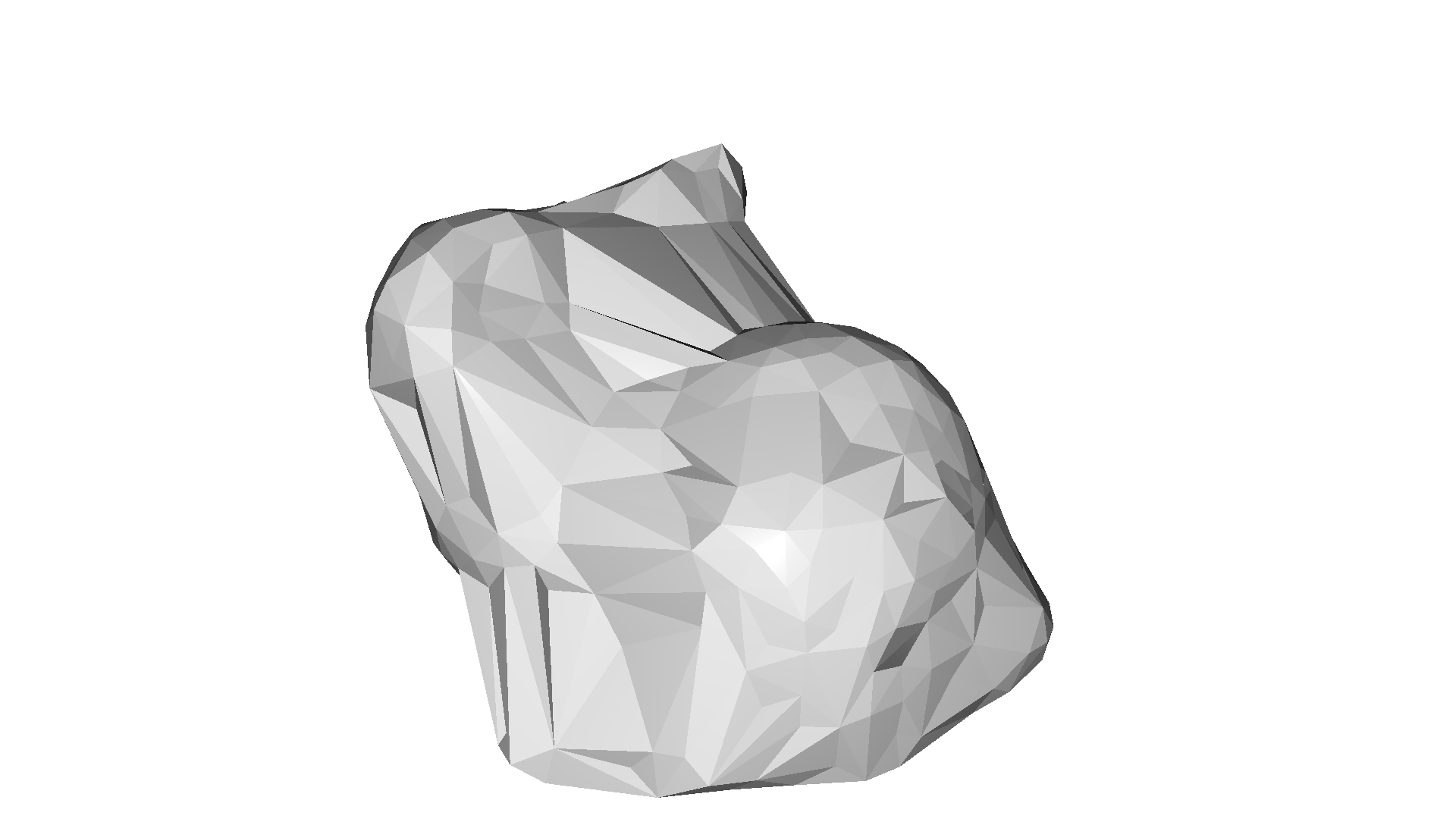

The implementation is based on the convex hull of the point cloud. If we want to compute multiple alpha shapes from a given point cloud, then we can save some computation by only computing the convex hull once and pass it to create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape.
[3]:
tetra_mesh, pt_map = cv3d.geometry.TetraMesh.create_from_point_cloud(pcd)
for alpha in np.logspace(np.log10(0.5), np.log10(0.01), num=4):
print(f"alpha={alpha:.3f}")
mesh = cv3d.geometry.ccMesh.create_from_point_cloud_alpha_shape(
pcd, alpha, tetra_mesh, pt_map)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_back_face=True)
alpha=0.500
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
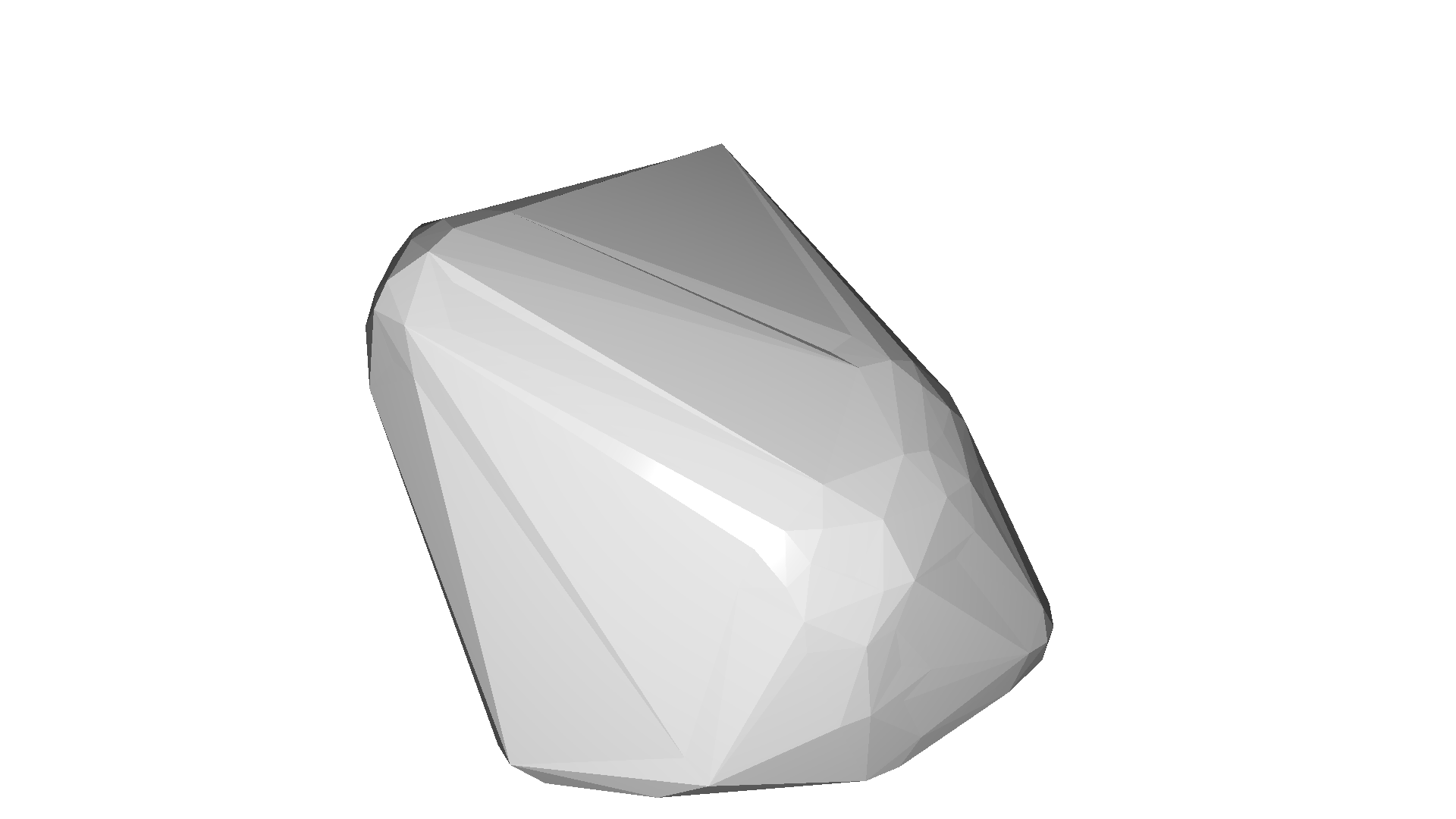

alpha=0.136
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
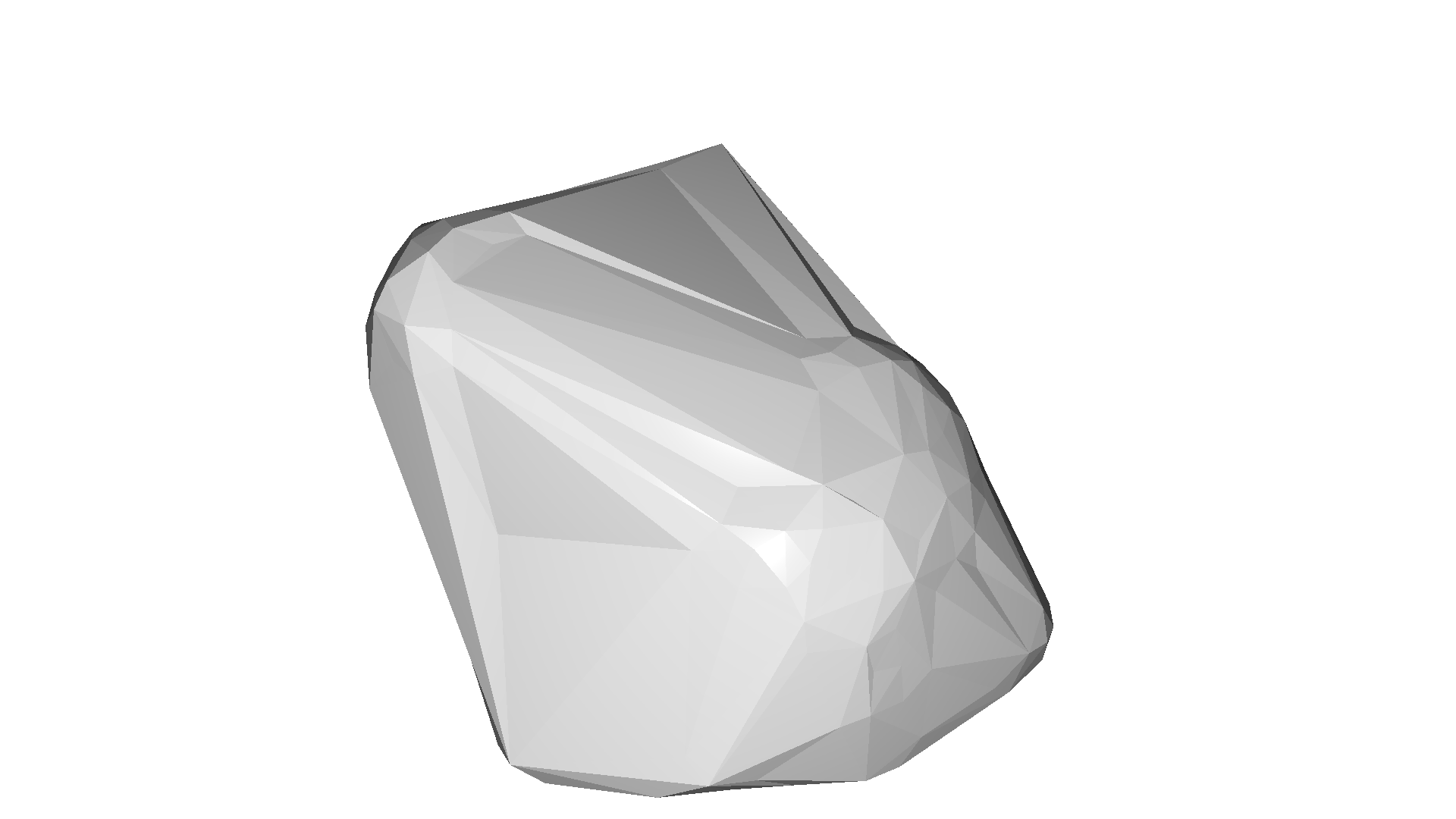

alpha=0.037
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
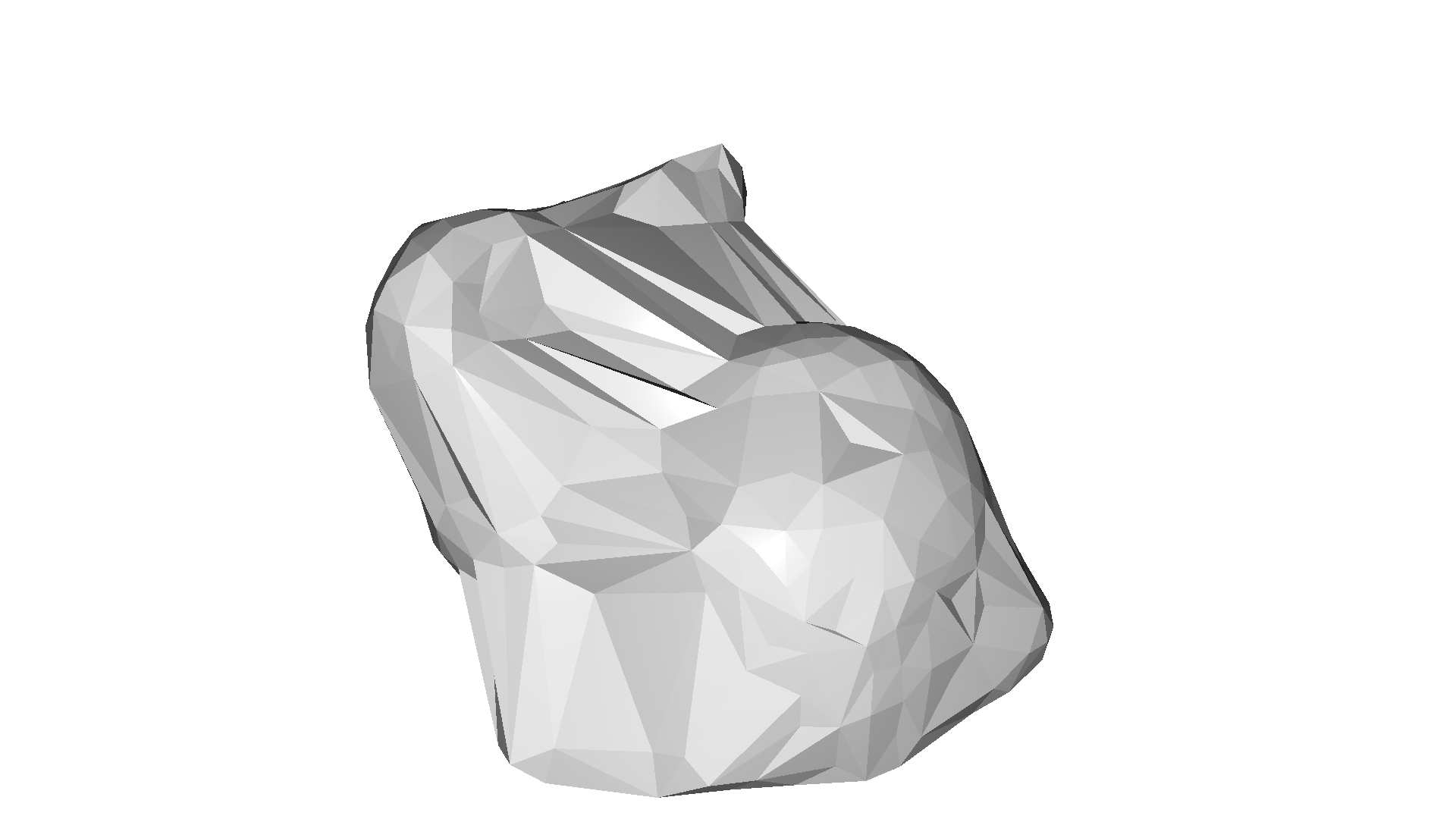

alpha=0.010
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
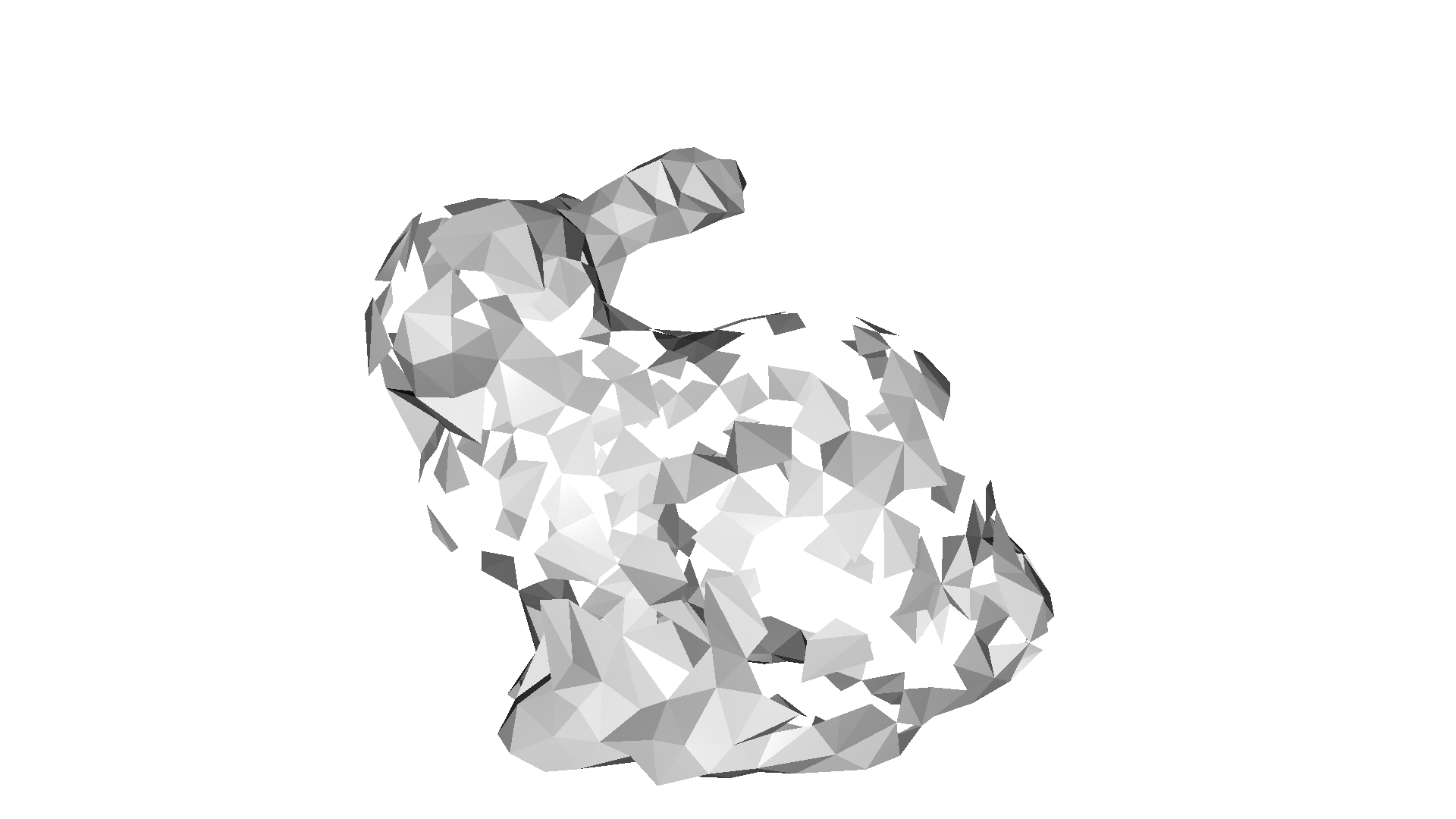

Ball pivoting#
The ball pivoting algorithm (BPA) [Bernardini1999] is a surface reconstruction method which is related to alpha shapes. Intuitively, think of a 3D ball with a given radius that we drop on the point cloud. If it hits any 3 points (and it does not fall through those 3 points) it creates a triangles. Then, the algorithm starts pivoting from the edges of the existing triangles and every time it hits 3 points where the ball does not fall through we create another triangle.
CloudViewer implements this method in create_from_point_cloud_ball_pivoting. The method accepts a list of radii as parameter that corresponds to the radii of the individual balls that are pivoted on the point cloud.
Note:
This algorithm assumes that the PointCloud has normals.
[4]:
bunny = cv3d.data.BunnyMesh()
gt_mesh = cv3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
gt_mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
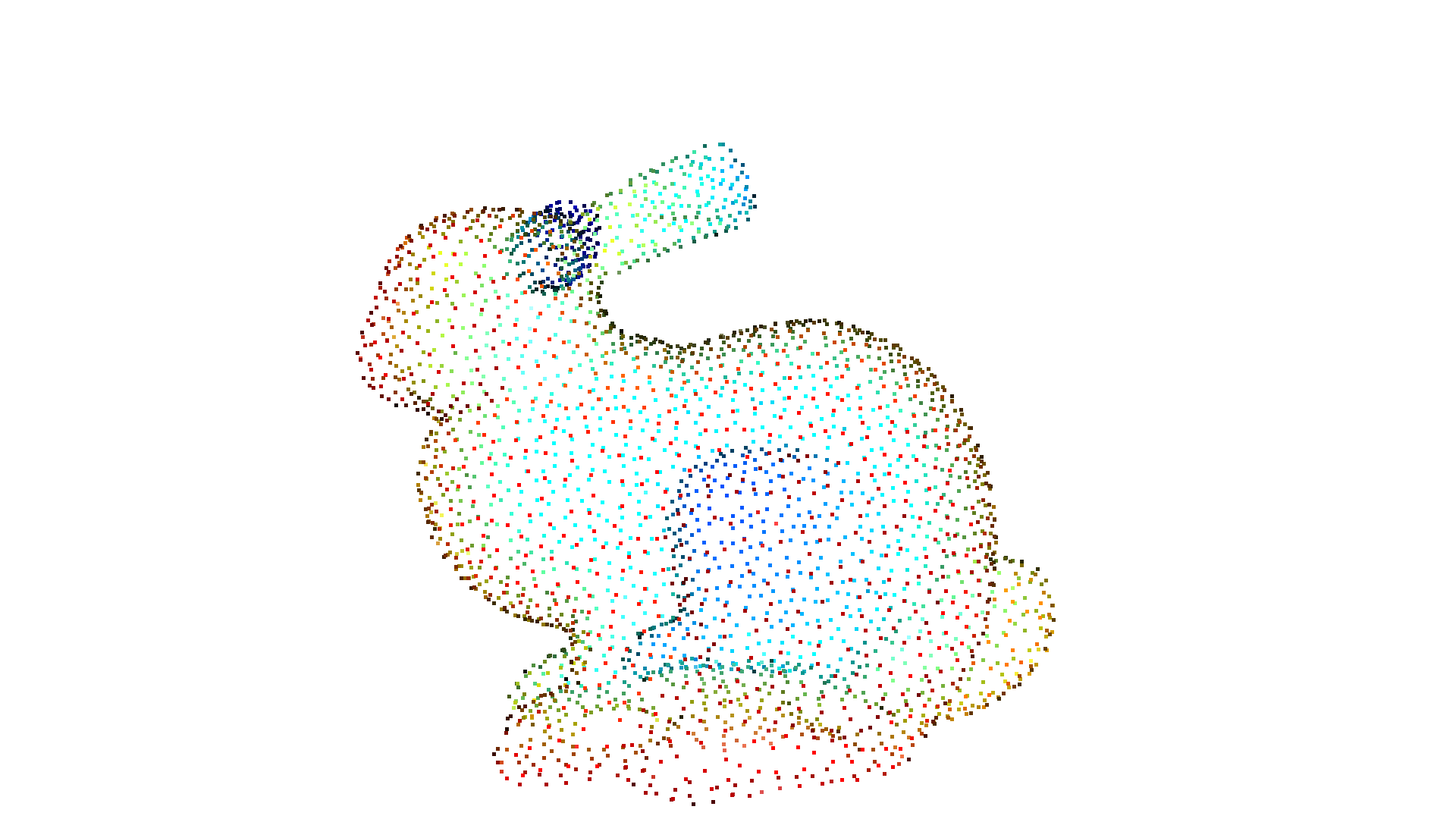
pcd = gt_mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(3000)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
[5]:
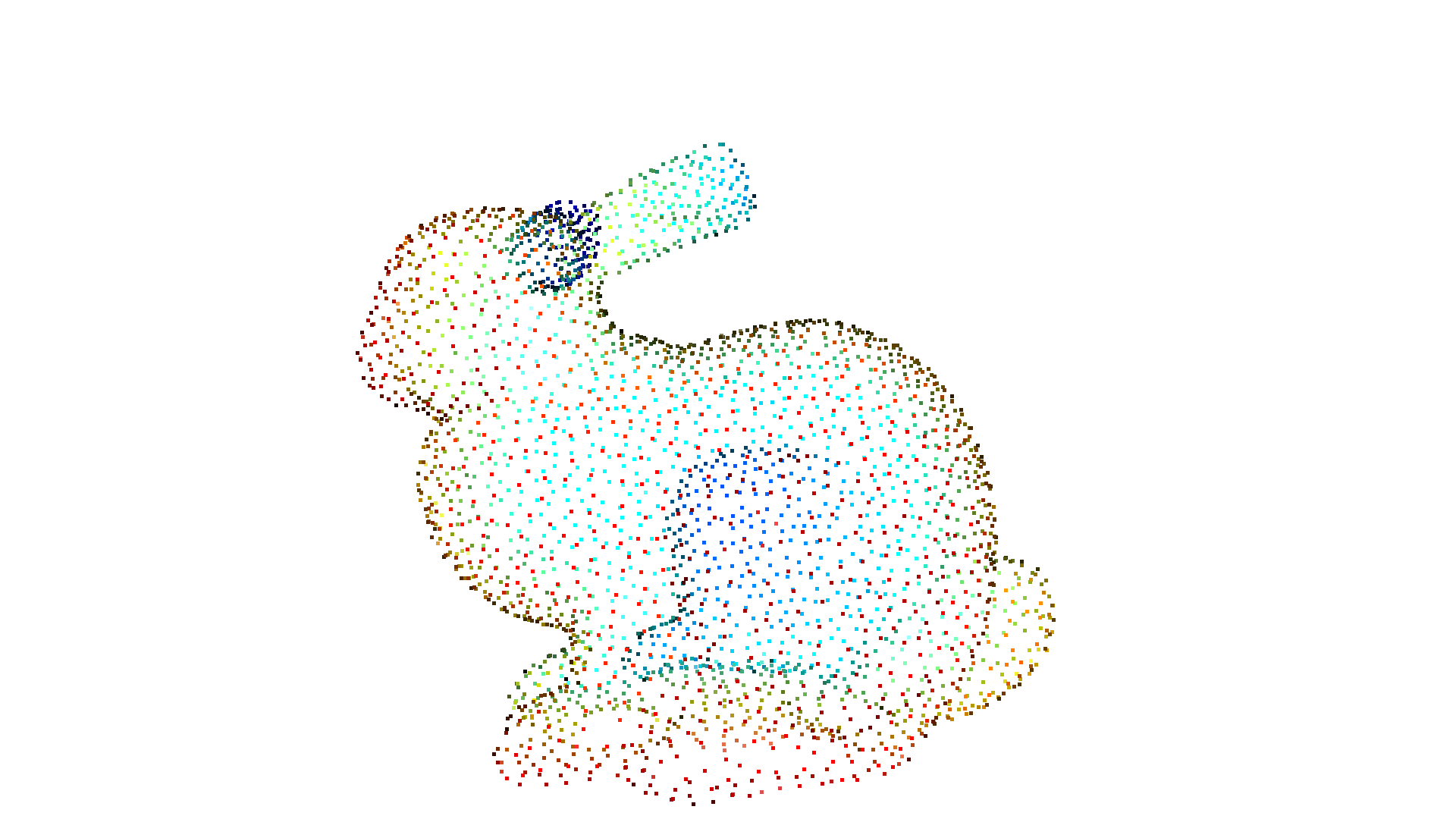
radii = [0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04]
rec_mesh = cv3d.geometry.ccMesh.create_from_point_cloud_ball_pivoting(
pcd, cv3d.utility.DoubleVector(radii))
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd, rec_mesh])
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
Poisson surface reconstruction#
The Poisson surface reconstruction method [Kazhdan2006] solves a regularized optimization problem to obtain a smooth surface. For this reason, Poisson surface reconstruction can be preferable to the methods mentioned above, as they produce non-smooth results since the points of the PointCloud are also the vertices of the resulting triangle mesh without any modifications.
CloudViewer implements the method create_from_point_cloud_poisson which is basically a wrapper of the code of Kazhdan. An important parameter of the function is depth that defines the depth of the octree used for the surface reconstruction and hence implies the resolution of the resulting triangle mesh. A higher depth value means a mesh with more details.
Note:
This algorithm assumes that the PointCloud has normals.
[6]:
eagle = cv3d.data.EaglePointCloud()
pcd = cv3d.io.read_point_cloud(eagle.path)
print(pcd)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd],
zoom=0.664,
front=[-0.4761, -0.4698, -0.7434],
lookat=[1.8900, 3.2596, 0.9284],
up=[0.2304, -0.8825, 0.4101])
[CloudViewer INFO] Downloading https://github.com/isl-org/open3d_downloads/releases/download/20220201-data/EaglePointCloud.ply
[CloudViewer INFO] Downloaded to /root/cloudViewer_data/download/EaglePointCloud/EaglePointCloud.ply
[CloudViewer WARNING] Destination is a directory: /root/cloudViewer_data/extract/EaglePointCloud
ccPointCloud with 796825 points.
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
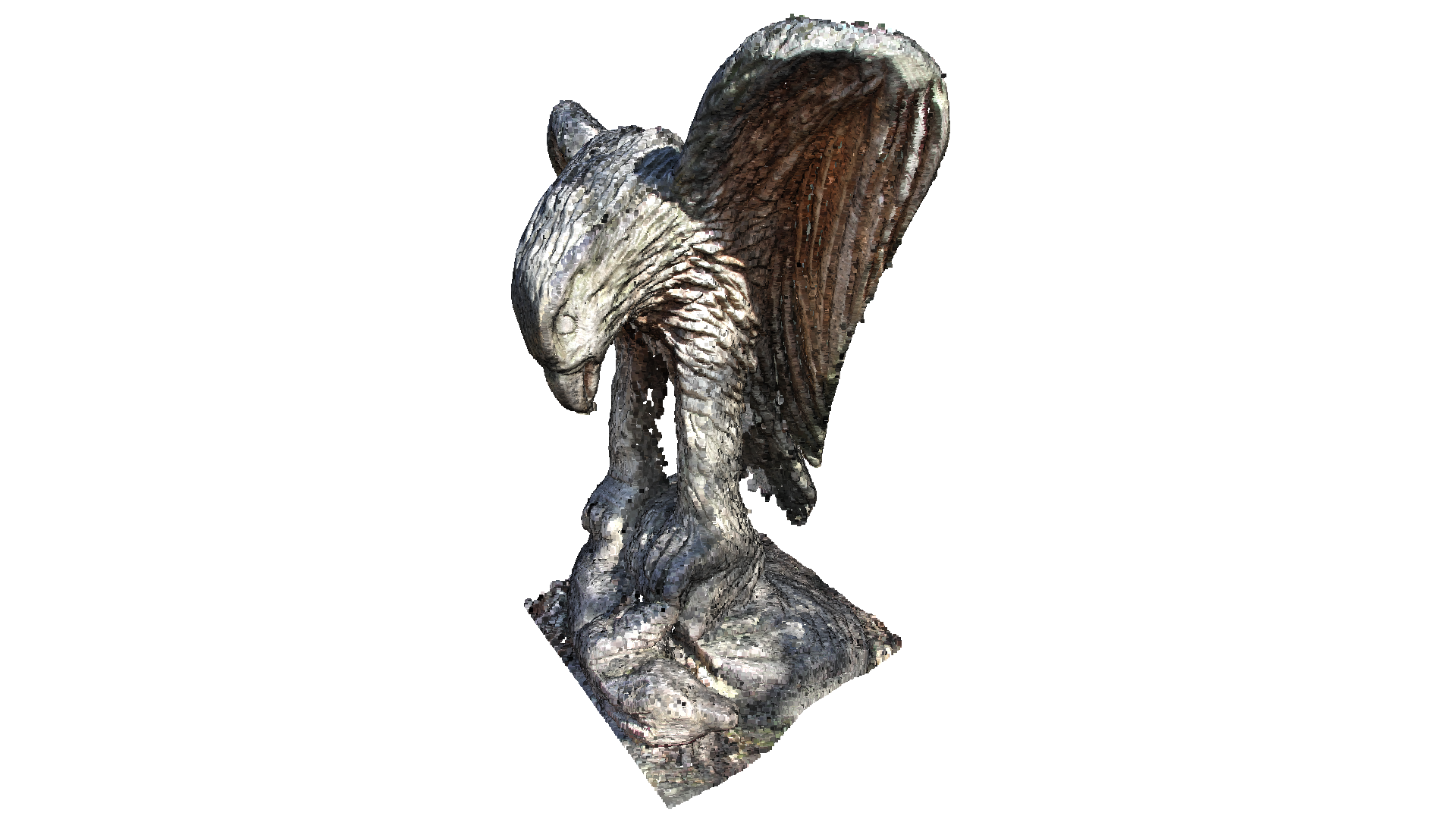

[7]:
print('run Poisson surface reconstruction')
with cv3d.utility.VerbosityContextManager(
cv3d.utility.VerbosityLevel.Debug) as cm:
mesh, densities = cv3d.geometry.ccMesh.create_from_point_cloud_poisson(
pcd, depth=9)
print(mesh)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh],
zoom=0.664,
front=[-0.4761, -0.4698, -0.7434],
lookat=[1.8900, 3.2596, 0.9284],
up=[0.2304, -0.8825, 0.4101])
run Poisson surface reconstruction
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Input Points / Samples: 796825 / 368254
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Got kernel density: 0.09464597702026367 (s), 365.5546875 (MB) / 365.5546875 (MB) / 476 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Got normal field: 0.6017172336578369 (s), 468.1796875 (MB) / 468.1796875 (MB) / 476 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Point weight / Estimated Area: 2.623550e-06 / 2.090510e+00
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Finalized tree: 0.5341858863830566 (s), 593.890625 (MB) / 593.890625 (MB) / 593 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Set FEM constraints: 1.5400691032409668 (s), 555.0546875 (MB) / 593.890625 (MB) / 593 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] #Set point constraints: 0.24662399291992188 (s), 555.0546875 (MB) / 593.890625 (MB) / 593 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Leaf Nodes / Active Nodes / Ghost Nodes: 2945433 / 3365000 / 1209
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Memory Usage: 555.055 MB
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Linear system solved: 2.167323112487793 (s), 595.06640625 (MB) / 595.06640625 (MB) / 595 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Got average: 0.08056497573852539 (s), 595.06640625 (MB) / 595.06640625 (MB) / 595 (MB)
[CloudViewer DEBUG] Iso-Value: 5.028478e-01 = 4.006817e+05 / 7.968250e+05
[CloudViewer DEBUG] # Total Solve: 9.8 (s), 739.8 (MB)
ccMesh with 563112 points and 1126072 triangles.
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
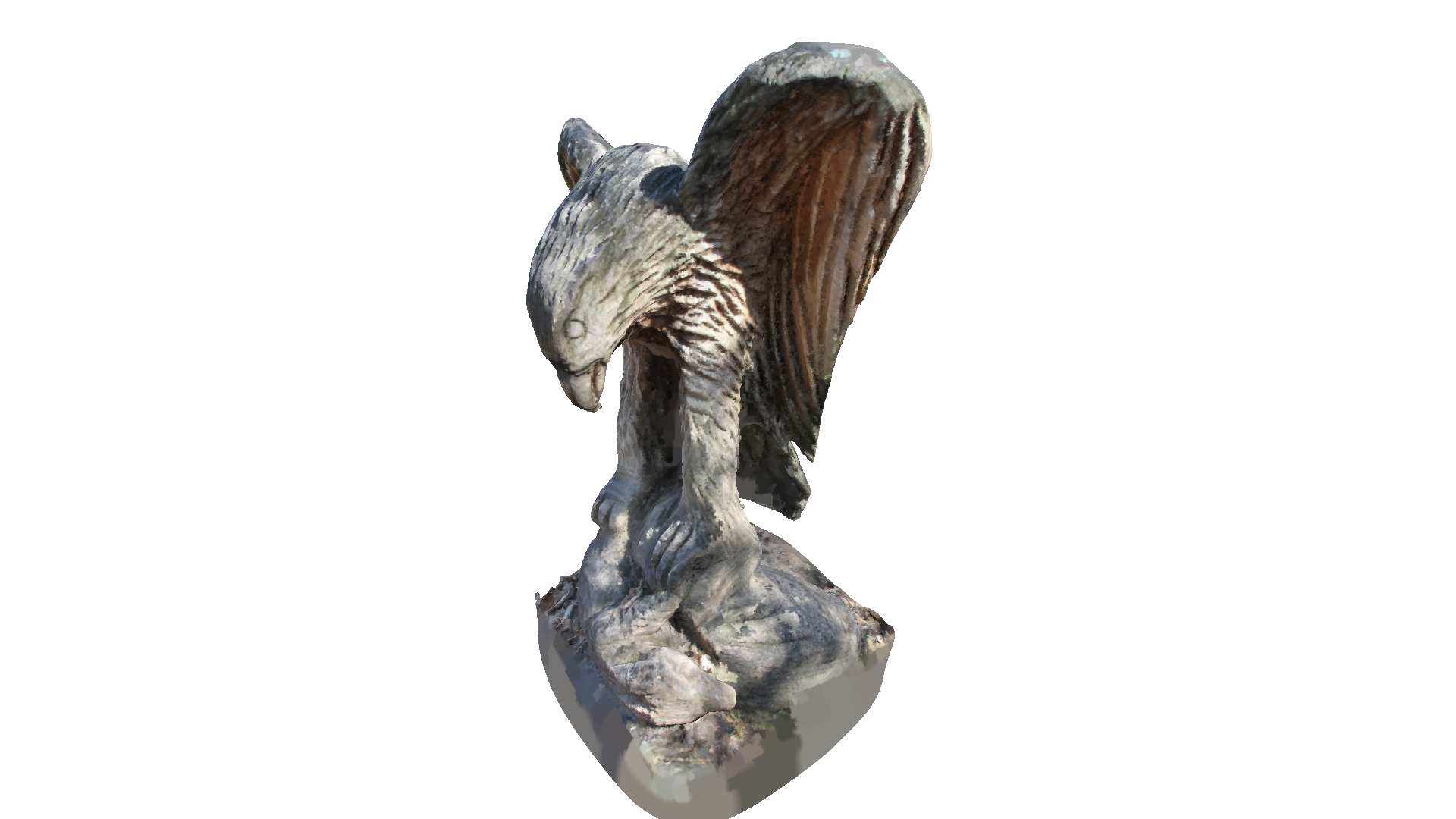

Poisson surface reconstruction will also create triangles in areas of low point density, and even extrapolates into some areas (see bottom of the eagle output above). The create_from_point_cloud_poisson function has a second densities return value that indicates for each vertex the density. A low density value means that the vertex is only supported by a low number of points from the input point cloud.
In the code below we visualize the density in 3D using pseudo color. Violet indicates low density and yellow indicates a high density.
[8]:
print('visualize densities')
densities = np.asarray(densities)
density_colors = plt.get_cmap('plasma')(
(densities - densities.min()) / (densities.max() - densities.min()))
density_colors = density_colors[:, :3]
density_mesh = cv3d.geometry.ccMesh()
density_mesh.create_internal_cloud()
density_mesh.set_vertices(mesh.get_vertices())
density_mesh.set_triangles(mesh.get_triangles())
density_mesh.set_vertex_colors(cv3d.utility.Vector3dVector(density_colors))
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([density_mesh],
zoom=0.664,
front=[-0.4761, -0.4698, -0.7434],
lookat=[1.8900, 3.2596, 0.9284],
up=[0.2304, -0.8825, 0.4101])
visualize densities
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
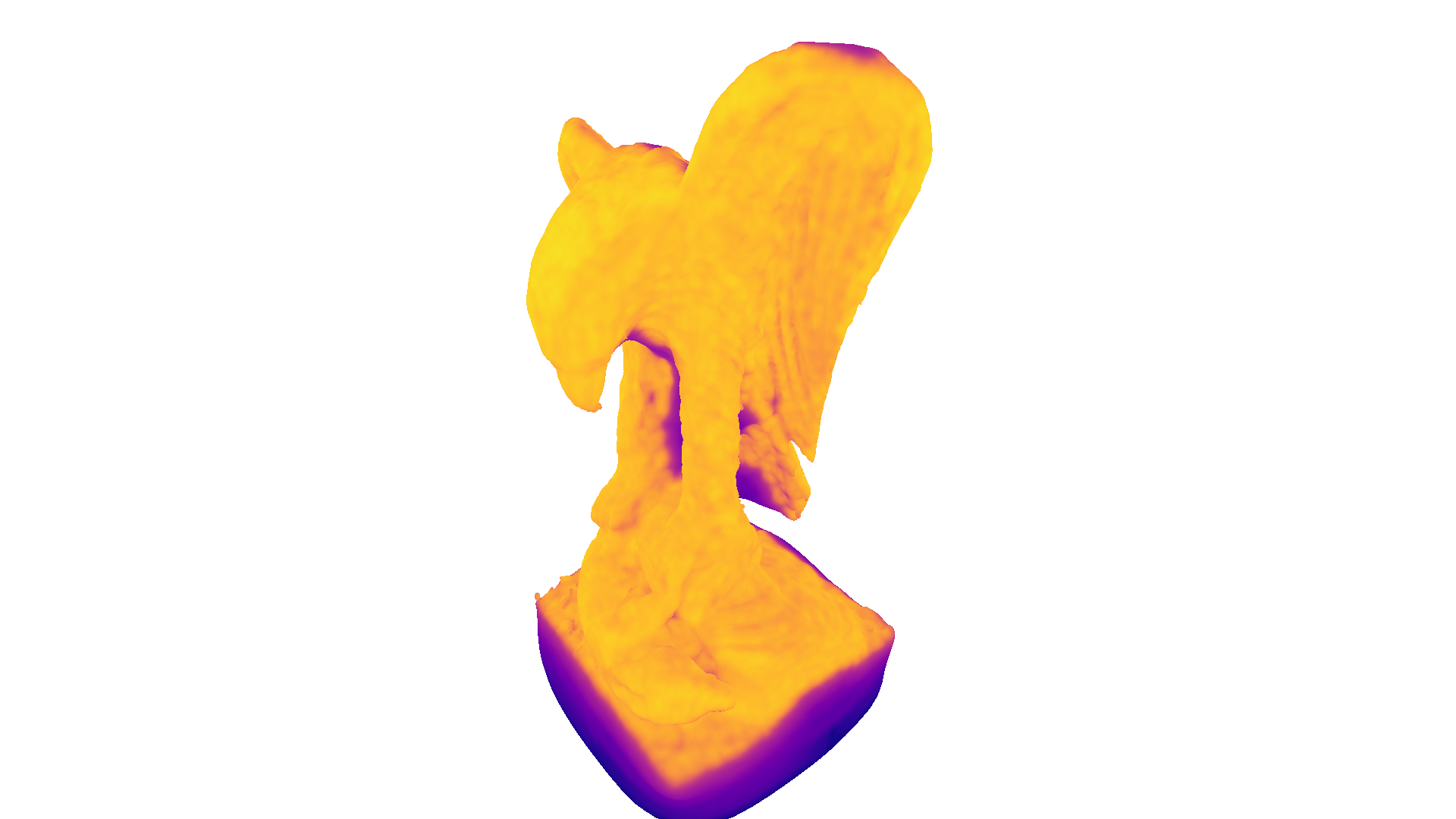
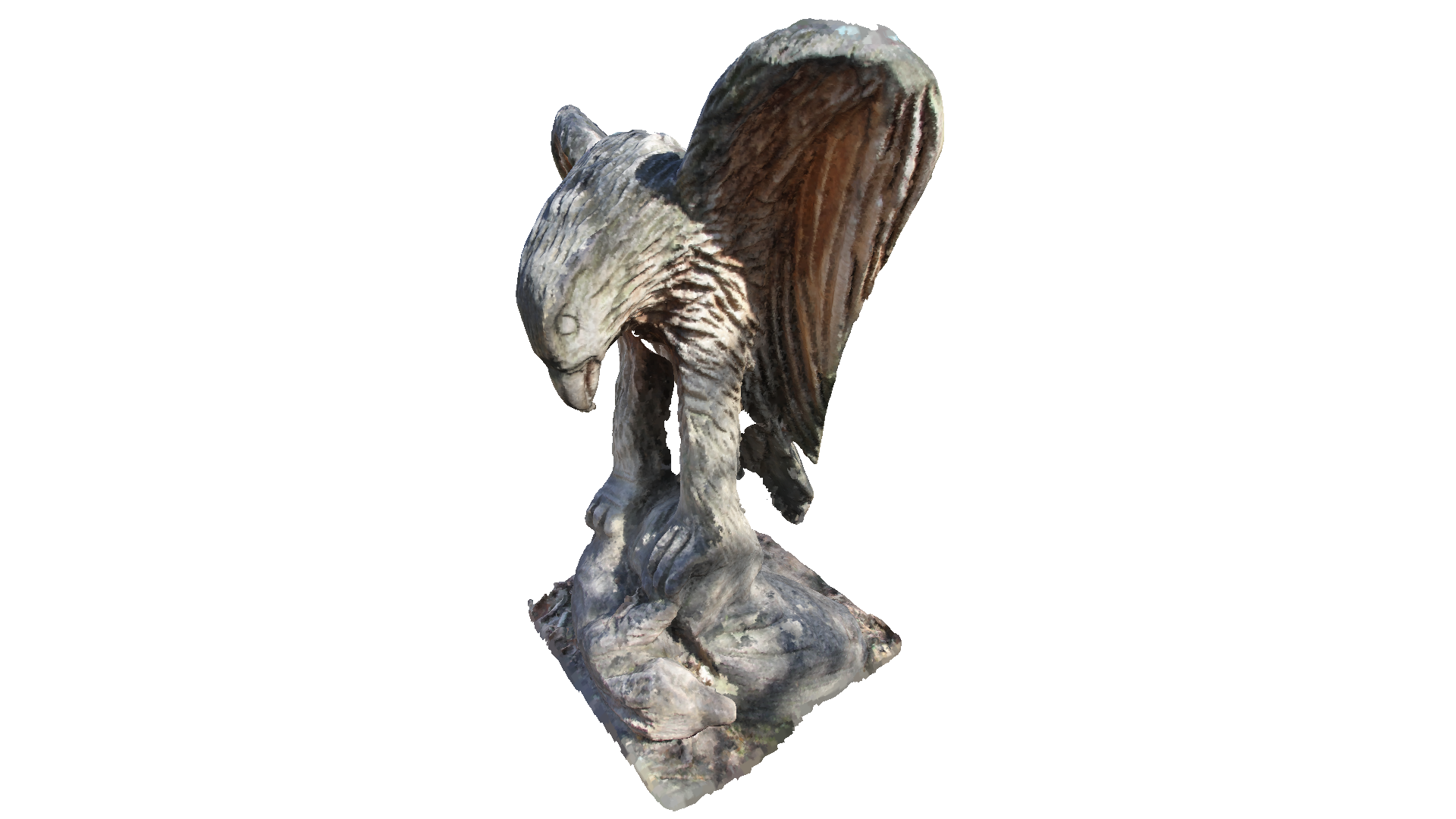
We can further use the density values to remove vertices and triangles that have a low support. In the code below we remove all vertices (and connected triangles) that have a lower density value than the \(0.01\) quantile of all density values.
[9]:
print('remove low density vertices')
vertices_to_remove = densities < np.quantile(densities, 0.01)
mesh.remove_vertices_by_mask(vertices_to_remove)
print(mesh)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh],
zoom=0.664,
front=[-0.4761, -0.4698, -0.7434],
lookat=[1.8900, 3.2596, 0.9284],
up=[0.2304, -0.8825, 0.4101])
remove low density vertices
ccMesh with 557480 points and 1113207 triangles.
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.

Normal estimation#
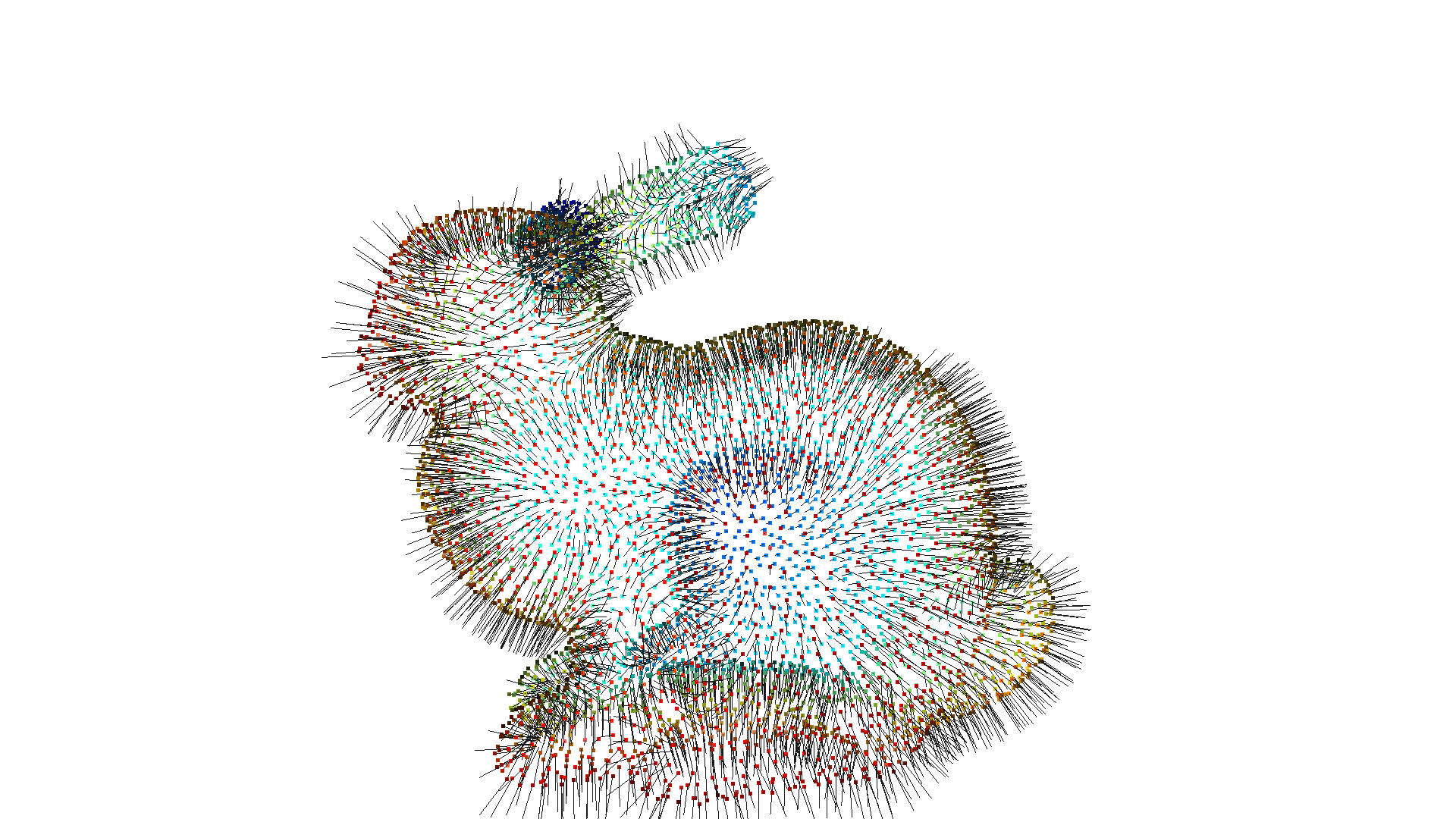
In the examples above we assumed that the point cloud has normals that point outwards. However, not all point clouds already come with associated normals. CloudViewer can be used to estimate point cloud normals with estimate_normals, which locally fits a plane per 3D point to derive the normal. However, the estimated normals might not be consistently oriented. orient_normals_consistent_tangent_plane propagates the normal orientation using a minimum spanning tree.
[10]:
bunny = cv3d.data.BunnyMesh()
gt_mesh = cv3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
pcd = gt_mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(5000)
pcd.set_normals(cv3d.utility.Vector3dVector(np.zeros(
(5000, 3)))) # invalidate existing normals
pcd.estimate_normals()
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd], point_show_normal=True)
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
[11]:
pcd.orient_normals_consistent_tangent_plane(100)
cv3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd], point_show_normal=True)
[CloudViewer WARNING] GLFW initialized for headless rendering.
